Postoperative Pulmonary Edema Due to Fluid Overload From an Infusion
What ICD-10-CM code s isare reports for postoperative pulmonary edema due to fluid overload as a complication of an infusion procedure. What ICD-9-CM code is reported for COPD with acute bronchitis.
The ICD-10-CM code E8770 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like anasarca.
. This phenomenon has been reported infrequently in the medical literature and may be underdiagnosed. Increased isotonic fluid retention. If a pt with ESRD presents w fluid overload due to noncompliance with dialysis fluid overload might be the PDX IF.
Postoperative complication like pulmonary edema is a consequence of excessive intraoperative fluid administration causing perioperative oxygen desaturation. ICD-10-CM E8770 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group s MS-DRG v390. It can result from decompensation of underlying heart failure acute coronary ischemia acute valvular disorder arrhythmia or acute volume overload.
Because the edema is due to the fluid overload that is associated with an infusion given during the patients medical care look in the ICD-10-CM External Cause of Injuries Index for Misadventure s to patient s during surgical. There are no known predictive warning signs and cardiorespiratory arrest is the most frequent clinical presentation. Thus cardiac issues were.
When the condition occurs the human body struggles to get sufficient oxygen and the patient starts to experience shortness of breath. The codes characterize the anatomical location of injury injury severity disease severity medical cause of injury etc. Pulmonary edema can result from an allergic reaction cardiac issue fluid overload or reaction to naloxone.
What ICD-9-CM codes are reported for postoperative pulmonary edema due to fluid overload from an infusion. In our case a large amount of fluid used for irrigation on the background of physiological changes of pregnancy led to intravasation and third spacing of fluid. What ICD-10-CM codes are reported for postoperative pulm onary edema due to fluid overload from an infusion.
A patient with AML Acute Myleogenous Leukemia has just learned his sister is an HLA match for him. The code E8770 is valid during the fiscal year 2022 from October 01 2021 through September 30 2022 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions. T8089XA J811 Y630 c.
T8089XA is the correct code choice. T8089XA Other complications following infusion transfusion J811 Chronic Pulmonary Edema E8779 Other Fluid Overload Y848 Medical procedure as cause. Pt has no HO CHF or evidence of CHF OR.
2 hours NPO led to pulmonary edema. Approx 400 ml in an hour versus a planned approximate of 75 ml1st hour. Pulmonary edema will be precipitated if there is either an increase in cardiac preload such as infusion of fluids or increased pulmonary capillary permeability such as in pre-eclampsia or both.
Patients were divided into three groups. 640 Miscellaneous disorders of nutrition metabolism fluids and electrolytes with mcc. Stem cells taken from the.
The correct ICD 10 code for postoperative pulmonary edema due to overload from an infusion is 5184 27669 E8730. 1519-21 In our patient the lack of rash or hives ruled out an allergic reaction. Pre- and post-operative cardiac examinations did not reveal a murmur and results of a telemetry electrocardiogram EKG scan did not raise concern for arrhythmia.
From the information gathered it was observed that postoperative cardiogenic pulmonary edema in patients with serious cardiovascular diseases is most common followed by noncardiogenic pulmonary edema which can be due to fluid overload in the postoperative period or it can be negative pressure pulmonary edema NPPE. Materials and Methods There were 13 study patients who from 1991 to 1996 had postoperative pulmonary edema documented by clinical criteria and characteristic findings on chest radiograph. The correct ICD 10 code for postoperative pulmonary edema due to overload from an infusion is 5184 27669 E8730.
Pulmonary edema can occur within the initial 36 postoperative hours when net fluid retention exceeds 67 mLkgd. Fluid retention overload or edema. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J681 became effective on October 1 2021.
Immediate recognition and t. Beyond the fluids Sukhen Samantaa Sujay Samantaa Abhishek Jhab Kajal Jainb Pulmonary edema PE after postpartum hemorrhage PPH resuscitation is mainly due to fluid overload or transfusion-related acute lung injury. In clinical practice it is usually suspected when a patient shows evidence of pulmonary edema peripheral edema or body cavity effusion.
E8770 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of fluid overload unspecified. Fatal cases of postoperative pulmonary edema in generally healthy individuals in whom the pulmonary edema was secondary to excessive fluid administra-tion. That postoperative cardiogenic pulmonary edema in patients with serious cardiovascular diseases is most common followed by noncardiogenic pulmonary edema which can be due to fluid overload in the.
Here we present the case of a 30-year-old primigravida having uncomplicated twin. Postoperative oxygen or mechanical ventilation may be needed 16 17 This increases postoperative morbidity mortality and treatment cost by increasing incidence of intensive care. The correct answer was given.
Fluid overload FO is characterized by hypervolemia edema or both. ICD codes are used for documentation of health conditions and medical procedures to support medical billing. A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes.
J810 E8770 Y631 b. Pulmonary edema is an abnormal buildup of fluid in the lungs. Postoperative pulmonary edema Of the seven patients with noncardiogenic postoperative pulmonary edema at least three cases were associated with documented laryngospasm causing upper airway obstruction.
J681 is a billablespecific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of J681 - other international versions of ICD-10 J681 may differ. Thus accidental fluid overload ie.
Postpartum pulmonary edema in twin parturient. Pulmonary Edema with CHF is coded to CHF unless the record explicitly states something such as Non-Cardiogenic Acute Pulmonary Edema. When defined as a gain 10 from their preoperative or premorbid weight or an approximately 20 increase in total body water 40 of patients had fluid overload.
Fluid levels were gradually lowered in infusion bottle to give a sense of pseudo security of fluid being delivered at appropriate rate whereas the fluid being delivered was at much higher rate. In the Tabular List this subcategory code requires seven characters. Abnormal increase in the volume of circulating fluid plasma in the body.
Those who had gained 10 those with a weight gain between 11 and 20 and those with 20 increase in weight. Next look for Edemalung directing you to J811. FO may be a consequence of spontaneous disease or may be a complication of intravenous fluid therapy.
How Does Fluid Overload Cause Heart Failure Can Fluid Overload Cause Pulmonary Edema Without Causing Heart Failure Quora
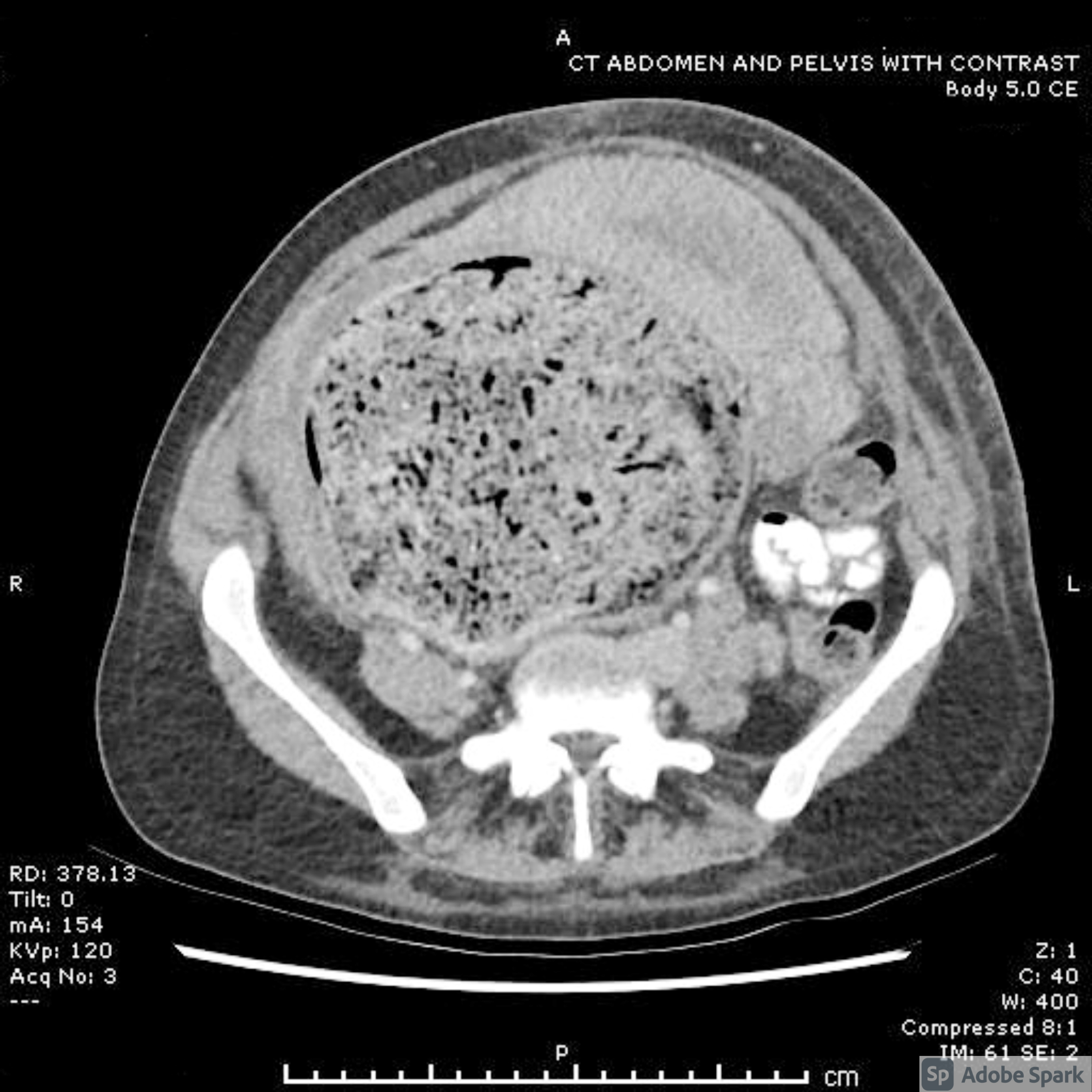
Cureus Acute Pulmonary Edema In Pregnancy Fluid Overload Or Atypical Pre Eclampsia
Pdf We Should Avoid The Term Fluid Overload

Postoperative Naloxone Induced Pulmonary Edema Consultant360

Iv Solutions Cheat Sheet Studypk Iv Solutions Nursing School Tips Nursing Notes

A Woman Who Developed Acute Pulmonary Edema During Operation A Case Report By R2 彭育仁 Ppt Video Online Download

A Depiction Of How Fluid Overload Can Lead To Interstitial Edema And Download Scientific Diagram

Pdf Diagnosis Prevention And Management Of Postoperative Pulmonary Edema

The Pathologic Tetrad Of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Ards Download Scientific Diagram

Nephrogenic Pulmonary Edema Acute Kidney Injury Triggers Numerous Download Scientific Diagram

Pulmonary Edema Fluid Levels Of Il 8 Are Inversely Associated With The Download Scientific Diagram

Pathophysiology Pulmonary Edema Ppt Download
How Does Fluid Overload Cause Heart Failure Can Fluid Overload Cause Pulmonary Edema Without Causing Heart Failure Quora
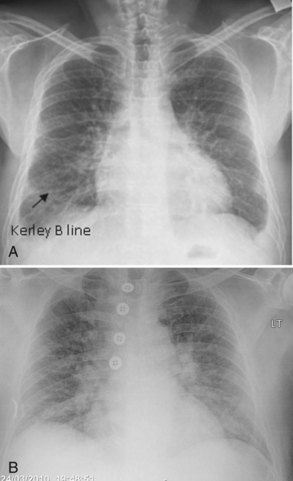
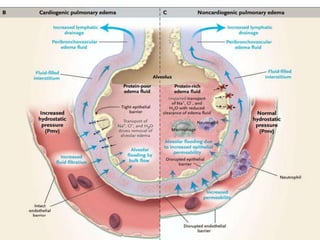
Comments
Post a Comment