Describe the Histology of Compact Bone
Compact bone is dense so that it can withstand compressive forces while spongy bone also called cancellous bone has open spaces and is supportive but also lightweight and can be readily remodeled to accommodate changing body needs. Describe the Describe the histology of compact bone including.
Seer Training Structure Of Bone Tissue
Again you may ask only the Haversian system or compact bone features or spongy bone structure.

. Compact bone is dense so that it can withstand compressive forces while spongy cancellous bone has open spaces and supports shifts in. The compact bone also has Volkmanns canal which lies at a right angle to the long axis of the bone and connects the blood and nerve supply from the. It is thick and dense.
Small cavity within bone matrix containing osteocytes. Compact bone slowly changes according to the stress tension and other mechanical forces. Trabecular bone also known as cancellous bone or spongy bone mainly serves a metabolic function.
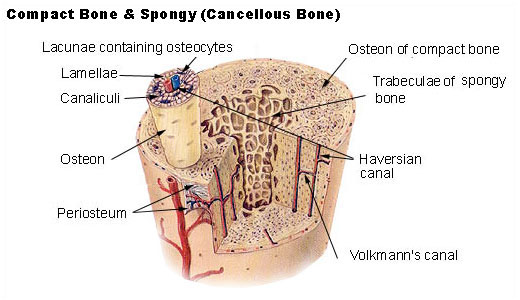
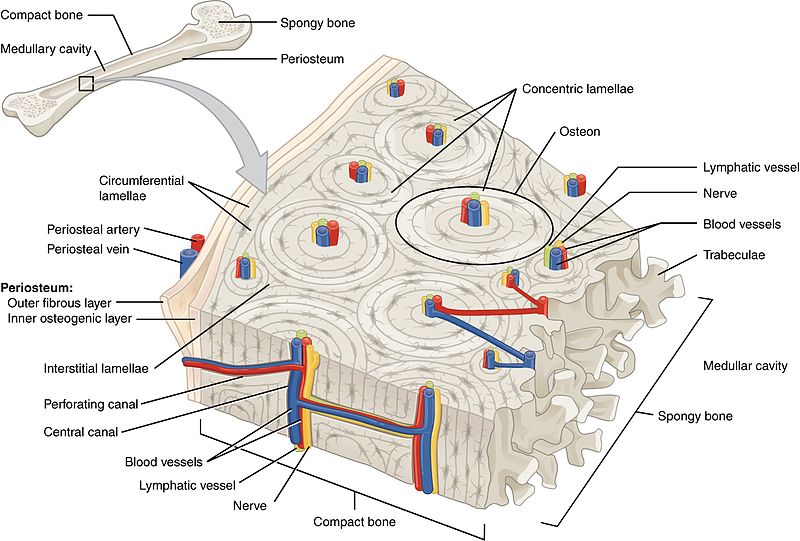
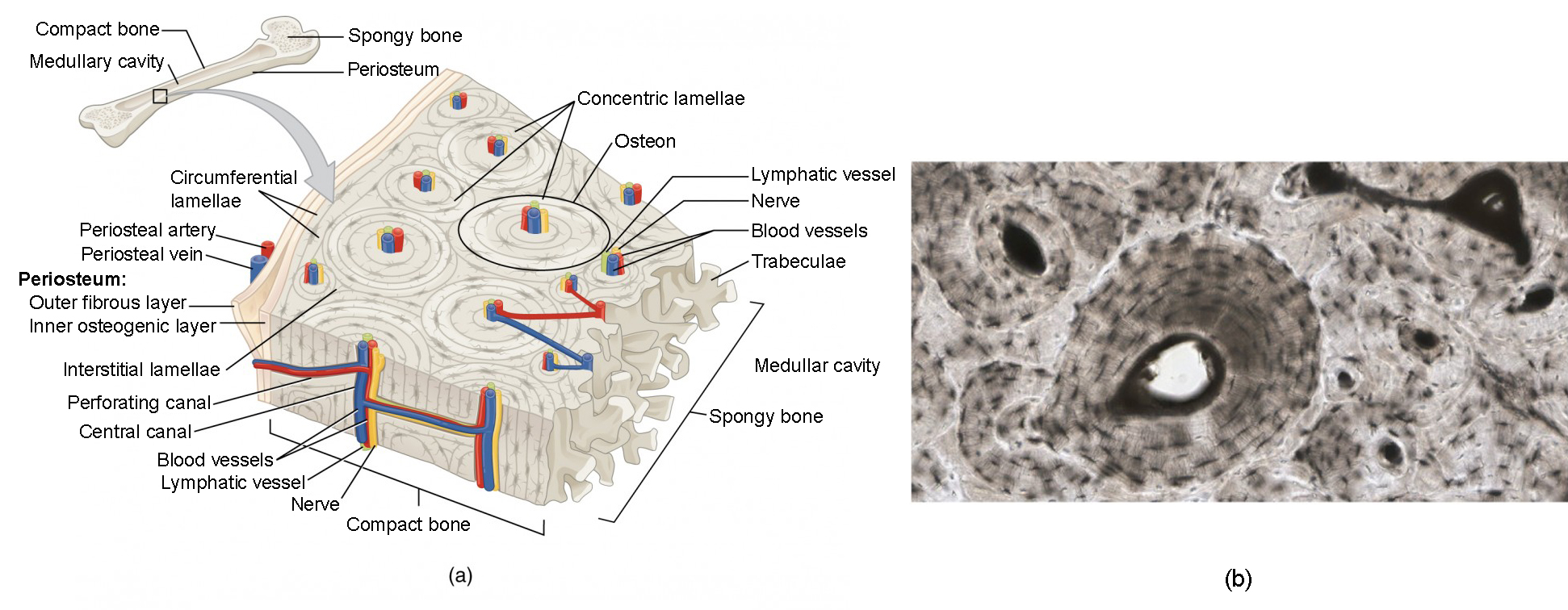
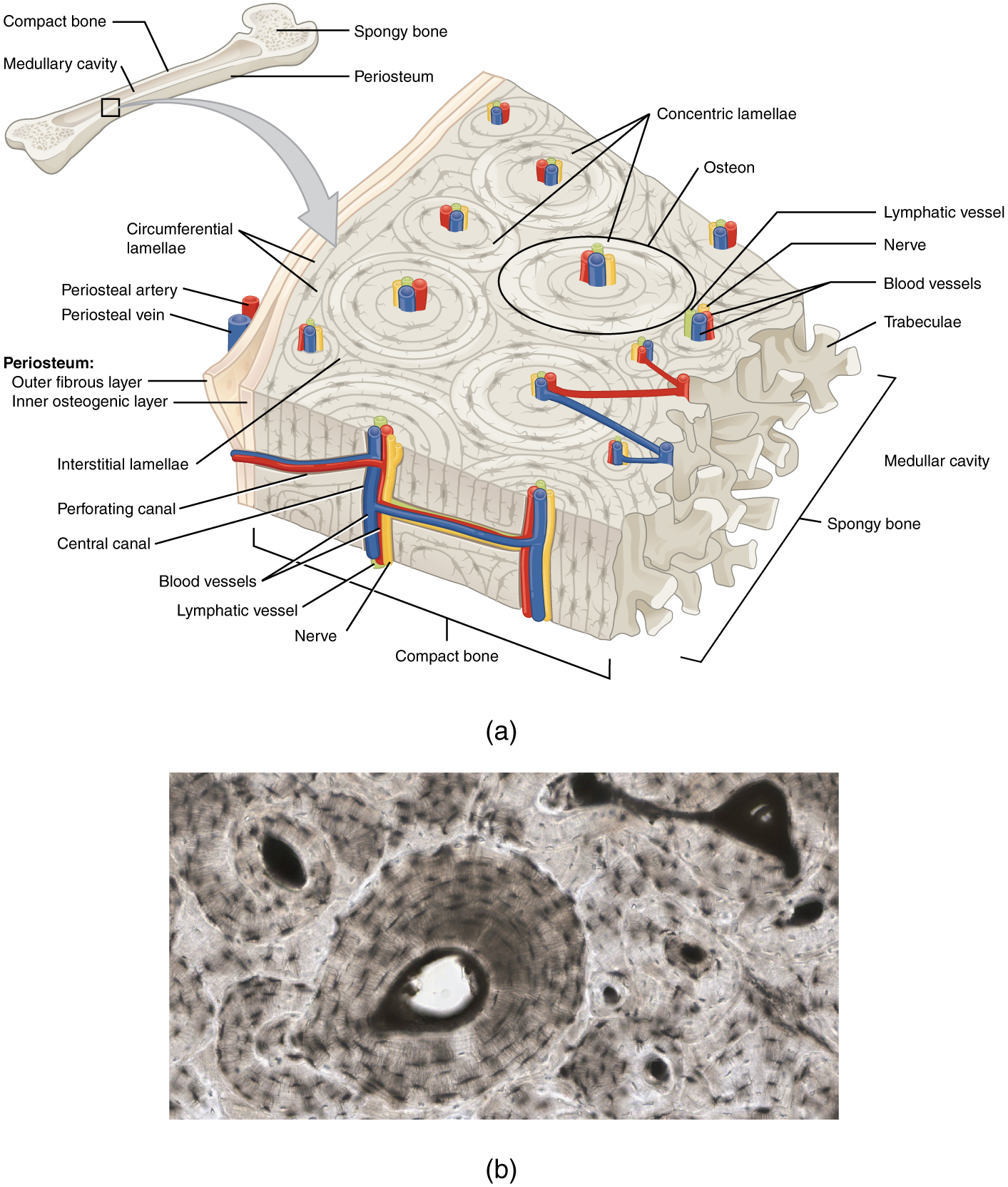
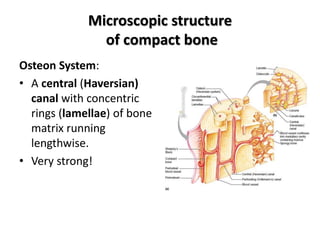
The basic structural and functional unit of mature compact bone lamellae. Compact bone also called cortical bone dense bone in which the bony matrix is solidly filled with organic ground substance and inorganic salts leaving only tiny spaces lacunae that contain the osteocytes or bone cells. Describe the histology of compact and spongy bone.
The compact bone is highly organized in osteons. Makes up part of the osteons. Compact bone dense cortical - high density - well organized - no trabeculae - external portion of bone 2.
Surrounded by concentric lamellae. Compact bone makes up 80 percent of the human skeleton. Compact bone appears solid and spongy bone consists of a web- or sponge-like arrangement of solidified extracelluar matrix.
Compare and contrast the mechanisms for the formation of. 2Compact View the full answer. -It contains a few spaces and is the strongest form of bone tissue.
It makes up the outer cortex. Bone tissue osseous tissue differs greatly from other tissues in the body. Bone is hard and many of its functions depend on that characteristic.
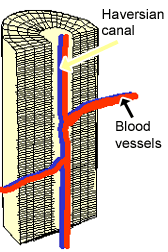
Spongy bone contains large marrow spaces defined by shelves and spicules of bone. This canal serves as passageway for blood vessels and nerves to move throughout the bone. -It provides protection and support and resists the stresses produced by weight and movement.
Ans1Compact and spongy bones are the two main types of osseous tissues. SPONGY BONE HISTOLOGY. Bone histology description.
The remainder is cancellous bone which has a spongelike appearance with numerous large spaces. If you asked to answer the bone histology you might write both compact substance and spongy substance histology. Bone cell formed when osteoblasts becomes embedded i the matrix it has secreted lacunae.
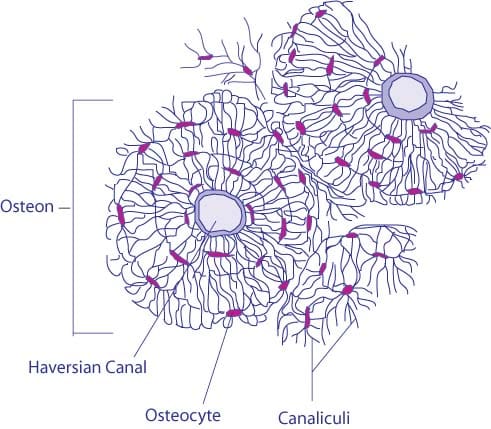
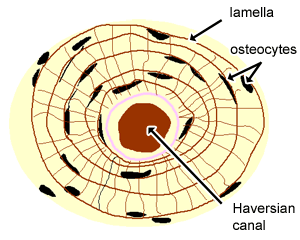
This is the area of bone to which ligaments and tendons attach. An osteon consists of tubes of bone matrix that surrounds a central Haversian canal. This type of bone is located between layers of compact bone and is thin and porous.
Osteons haversian systems Repeating structural units. I think you have a great idea of the different bone cells osteocytes osteoblast and osteoclast. Most bones contain compact and spongy osseous tissue but their distribution and concentration vary based on the bones overall function.
Compact Bone Tissue. Outside all of bone is a connective tissue sheath called the periosteum see below photograph. Trabecular bone spongy cancellous - low density - trabeculae bony spicules with marrow in between - internal part of bone Describe the formation of bone intramembranous vs.
Identify the structures that compose compact and spongy bone. Which contain a centrally located Haversian. Thin layer membrane or plate of tissue in bone central canal.
While compact bone appears at first glance to be solid and uninterrupted closer inspections reveals that the osseous tissue only makes up from 70-95 of the available volume. The structure gives a sponge-like appearance so this type of. Describe how bones are nourished and innervated.
Compact bone or cortical bone mainly serves a mechanical function. -It is present beneath the periosteum of all bones and forms the bulk of the diaphyses. Osteocytes can be seen in layers in adult spongy bone.
Compare and contrast compact and spongy bone. Spongy bone is the osseous tissue which fills the interior cavity of bones consisting of mineralized bars called trabeculae. The ends of the long bones are devoid of the marrow cavity.
Name and describe the 4 different cell types associated with bone. Cerebrospinal fluid filled space that runs through spinal cord osteocytes. Compact bone is the denser stronger of the two types of osseous tissue Figure 636.
A Perforating or Volkmanns canals lie at right angles to the long axis of the bone and. 7 rows The functional units of compact bone are osteons. There are pores and spaces even in compact bone.
The differences between compact and spongy bone are best explored via their histology. 1 The structural unit of compact bone is the osteon or Haversian system which consists of concentric tubes of bone matrix the lamellae surrounding a central Haversian canal that serves as a passageway for blood vessels and nerves. It is found beneath the periosteum of all bones and makes up the bulk of the diaphyses of long bones.
Compact bone is the non-cancellous portion of a bone which largely consists of closely packed osteons and forms the hard exterior of the bone. The strongest form of bone tissue. It contains numerous minute spaces.
Central canal lacunae canaliculi lamellae circumferential. The inner space is lined by osteoblasts and osteoclasts called the endosteum. Instead they are populated with mesh-like structure made up of plates and rods.
Describe the histology of bone tissue.
Cartilage Bone Ossification The Histology Guide
Cartilage Bone Ossification The Histology Guide

Bone Tissue Supportive Connective Tissue Ppt Download
Ultrastructure Of Bone Components Structure Teachmeanatomy
14 4 Structure Of Bone Biology Libretexts

Compact Bone Histology Circumferential Interstitial And Haversian System Anatomylearner The Place To Learn Veterinary Anatomy Online

Compact Bone Definition Structure Function Facts Britannica
Bone Structure Anatomy And Physiology I

Endosteum Definition Function Histology Vs Periosteum Anatomy Bones Skeletal System Anatomy Bones Human Body Projects
Bone Structure Anatomy And Physiology

5 3 Bone Structure Medicine Libretexts
Compact Bone Spongy Bone And Other Bone Components Human Anatomy And Physiology Lab Bsb 141
Cartilage Bone Ossification The Histology Guide

Figure Histological Description Of Trabecular And Cortical Bone Download Scientific Diagram

Compact Bone Histology Circumferential Interstitial And Haversian System Anatomylearner The Place To Learn Veterinary Anatomy Online



Comments
Post a Comment